Commercial dishwashing operations require a sophisticated understanding of chemistry, safety protocols, and cost optimization to maintain both hygiene standards and operational efficiency. The selection of appropriate chemicals—including detergents, sanitizers, rinse aids, and descalers—directly impacts cleaning performance, equipment longevity, and regulatory compliance. This comprehensive guide provides practical insights based on industry experience and authoritative sources to help foodservice professionals make informed decisions about their warewashing chemical programs.
Understanding the Foundation of Commercial Dishwasher Chemistry
Commercial dishwashing differs fundamentally from residential applications in both scale and regulatory requirements. Professional kitchens must achieve a minimum 99.999% bacteria reduction (5-log reduction) while processing hundreds of dishes per hour under stringent health department oversight. The chemistry behind effective commercial warewashing involves four critical components working in harmony: detergents for soil removal, sanitizers for microbial elimination, rinse aids for spot-free drying, and descalers for equipment maintenance.
Water quality significantly influences chemical performance, with factors such as hardness, pH, and temperature affecting both cleaning efficacy and chemical consumption rates. Hard water conditions, common in many regions, can reduce detergent effectiveness and increase mineral buildup, requiring specialized formulations and adjusted dosing protocols. Understanding these variables is essential for optimizing chemical programs and controlling operational costs.
Essential Chemical Categories and Their Applications
Commercial Detergents: The Primary Cleaning Workhorses
Commercial dishwasher detergents serve as the foundation of any effective warewashing program, designed to remove grease, food residue, protein soils, and starch-based deposits. These formulations typically contain alkaline compounds that break down organic soils, surfactants that reduce surface tension for better soil penetration, builders that soften water and enhance cleaning action, and enzymes that target specific soil types.
Liquid detergents dominate the commercial market due to their ease of handling and consistent dosing characteristics. Leading manufacturers like Ecolab offer comprehensive liquid programs such as their Trump dishwasher detergent, which provides alkaline, NTA, EDTA, phosphate-free, and chlorine-free formulations guaranteed to deliver one-pass cleaning results. Kay Chemical, a division of Ecolab, specializes in QSR (Quick Service Restaurant) applications with products like their machine warewashing detergent that maintains optimal performance in high-volume, fast-paced environments.
Powder detergents remain popular in high-temperature applications where their concentrated formulations and bleaching action provide superior stain removal on plastic and china tableware. However, powder systems require careful water quality management and proper dissolving conditions to prevent residue buildup and ensure consistent performance.
Sanitizers: Meeting Health Code Requirements
Sanitization represents the most critical aspect of commercial dishwashing from a food safety perspective. Low-temperature dishwashers, operating at 120°F rinse temperatures, rely entirely on chemical sanitizers to achieve required microbial reduction levels. High-temperature machines, while achieving sanitization through 180°F final rinse temperatures, often incorporate chemical sanitizers for additional safety margins.
Chlorine-based sanitizers, primarily sodium hypochlorite solutions, remain the most widely used due to their broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity and cost-effectiveness. These products typically require 25-100 ppm concentration depending on water conditions and must maintain contact times of 10 seconds minimum. Advantage Chemicals’ low-temperature concentrated sanitizer exemplifies industry-standard chlorine products, providing effective sanitization at 100 ppm while offering stain removal benefits on plastic and china surfaces.
Quaternary ammonium (quat) sanitizers offer advantages in specific applications, particularly where chlorine’s corrosive effects on soft metals pose concerns. These products provide 100-400 ppm active concentration with 30-second contact times and leave antimicrobial residues that continue protecting surfaces after drying. P&G Professional’s Broad Range Quaternary Sanitizer demonstrates the versatility of quat systems for both machine dishwashing and surface sanitization applications.
Rinse Aids: Achieving Spot-Free Results
Rinse aids represent perhaps the most underappreciated component of commercial dishwashing chemistry, yet their impact on customer satisfaction and operational efficiency cannot be overstated. These products contain nonionic surfactants and alcohol alkoxylates that dramatically reduce water surface tension, promoting rapid water sheeting and preventing the formation of water spots and streaks.
The mechanism of rinse aid action involves modifying the final rinse water’s behavior on clean surfaces. Without rinse aids, water forms droplets that evaporate slowly, leaving mineral deposits that create unsightly spots and require rewashing. Professional rinse aids ensure that water flows off surfaces in thin sheets, carrying away dissolved minerals and reducing drying times.
Winterhalter’s dosing technology exemplifies the precision required for optimal rinse aid performance. Their peristaltic pump systems deliver exact quantities based on water quality and cycle parameters, ensuring consistent results while minimizing chemical waste. Proper rinse aid dosing typically requires 0.5-2.0 mL per rack depending on water hardness and dishwasher type.
Descalers and Delimers: Equipment Protection and Maintenance
Scale and mineral buildup represent ongoing challenges in commercial dishwashing operations, particularly in areas with hard water. Descaling products contain acid-based formulations, typically phosphoric acid, citric acid, or hydrochloric acid, designed to dissolve calcium and magnesium deposits without damaging stainless steel equipment.
Regular descaling protocols vary by water hardness and usage volume but typically require monthly to quarterly applications. The descaling process involves circulating diluted descaler through the dishwasher’s wash and rinse systems for specified contact times, followed by thorough rinsing to remove dissolved scale and acid residues.
Vista descaler products demonstrate industry-standard formulations that recommend 4-8 ounces per gallon for light to medium buildups and 8 ounces per gallon for heavy deposits 24. Modern dishwashers often incorporate automatic descaling cycles that guide operators through the process while ensuring proper dilution and contact times.
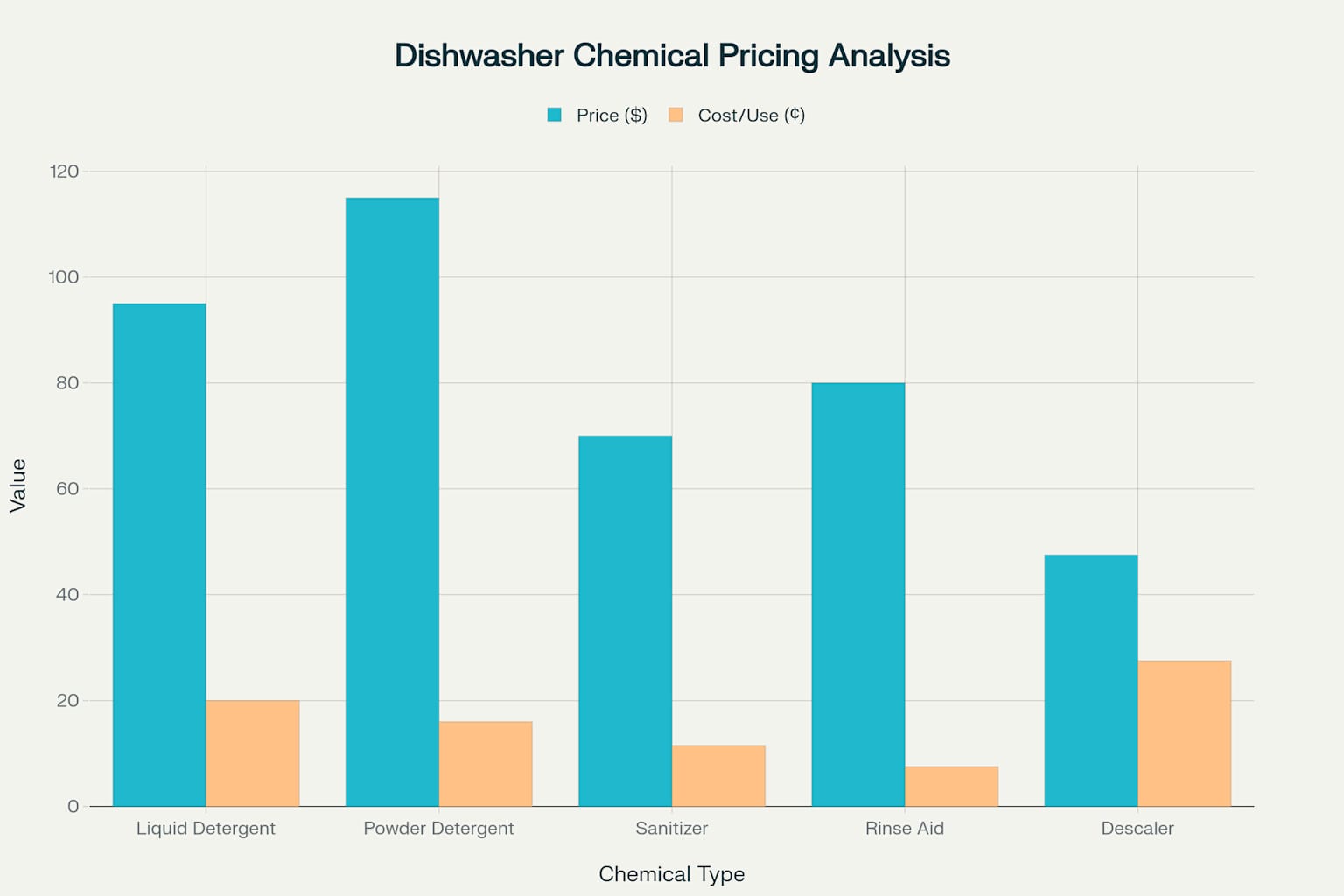
Comparative analysis of pricing and cost-per-use for different types of commercial dishwasher chemicals
Safety Protocols and Regulatory Compliance
Chemical safety in commercial kitchens requires comprehensive protocols covering storage, handling, personal protective equipment, and emergency procedures. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) provide essential information about chemical hazards, safe handling procedures, and emergency response measures. Federal regulations require MSDS availability for all commercial cleaning chemicals, and kitchen managers must ensure staff access and understanding.
Personal protective equipment requirements vary by chemical type and concentration but universally include chemical-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and protective clothing. Warewashing chemicals can cause severe skin and eye damage upon contact, making proper PPE usage non-negotiable. Ventilation requirements ensure adequate air circulation to prevent vapor accumulation and protect workers from respiratory irritation.

Commercial dishwasher chemical safety and handling infographic
Chemical compatibility represents a critical safety consideration, as mixing different chemical types can create dangerous reactions. Never combine chlorine sanitizers with acid-based products, as this reaction produces toxic chlorine gas. Similarly, mixing different brands or types of chemicals can neutralize effectiveness or create unexpected hazards.
Storage protocols require chemical separation from food products, proper labeling of dispensing containers, and maintenance of appropriate temperatures and ventilation. Many commercial chemicals require storage below 80°F to maintain stability and effectiveness.
Cost Analysis and Program Optimization
Commercial dishwashing chemical costs typically represent 15-20% of total warewashing expenses, making optimization efforts financially significant. Understanding cost-per-use calculations helps operators evaluate different products and suppliers objectively.
Liquid detergents generally cost $0.15-0.25 per wash cycle, while powder detergents offer slightly lower per-use costs at $0.12-0.20 due to their concentrated nature.
Sanitizers represent the most cost-effective chemical category at $0.08-0.15 per cycle, while descalers show higher per-use costs at $0.20-0.35 due to their periodic application schedule.
Automatic dosing systems significantly impact long-term costs by ensuring precise chemical delivery and eliminating waste from over-dosing. Winterhalter’s Quantura dosing systems demonstrate how technology can optimize chemical consumption while maintaining consistent results. These systems typically pay for themselves within 6-12 months through reduced chemical consumption and improved wash quality.
Implementation Best Practices and Professional Recommendations
Successful chemical program implementation requires systematic evaluation of operational needs, water quality assessment, and staff training protocols. Begin with comprehensive water testing to determine hardness, pH, and mineral content, as these factors directly influence chemical selection and dosing requirements.
Establish relationships with reputable suppliers who provide technical support, training resources, and emergency chemical delivery services. Companies like Ecolab, Diversey, and P&G Professional offer comprehensive support programs that extend beyond product sales to include equipment maintenance and staff education.
Monitor wash quality through regular testing of sanitizer concentrations, visual inspection of cleaned items, and customer feedback regarding spotting or residue issues. Implement documentation systems that track chemical consumption, wash quality metrics, and equipment maintenance schedules to identify optimization opportunities.
Training programs should cover proper chemical handling, safety protocols, and troubleshooting procedures for common issues. Regular refresher training ensures continued compliance and optimal performance as staff turnover occurs.
Conclusion
Selecting optimal chemicals for commercial dishwashing operations requires balancing performance, safety, cost, and regulatory compliance considerations. Success depends on understanding the unique chemistry of each product category, implementing proper safety protocols, and maintaining ongoing optimization efforts. By following evidence-based selection criteria and working with reputable suppliers, foodservice operations can achieve superior wash quality while controlling costs and ensuring regulatory compliance. The investment in proper chemical programs pays dividends through improved customer satisfaction, reduced rewash rates, and extended equipment life.

